
Thus, immunotherapies, and in this case anti METH immunotherapy, can provide broad neuroprotection to all sites of action in the central nervous system without causing any adverse effects in the brain.Īnti-METH monoclonal antibodies have the ability decrease brain concentrations of METH, reduce METH-induced behavioral effects such as locomotor activity, and have been shown to reduce the rate of self administration in rat models of METH abuse. Moreover, since antibodies have extremely high affinities for their target ligand and do not cross the blood-brain barrier, they significantly lower drug concentrations in the central nervous system. Unlike conventional receptor agonists or antagonists for treatment of drug abuse, antibodies have exquisite ligand or ligand class specificity and do not interfere with the actions of endogenous ligands or neurotransmitters, which can lead adverse effects. By removing a drug from its sites of action or preventing it from reaching target sites, antibodies act as pharmacokinetic antagonists. However, specific FDA-approved medications designed to treat the medical complications of METH abuse do not exist.ĭrug-specific immunotherapy is a promising approach to treating the adverse health effects of drug use for many important drugs of abuse, including nicotine, PCP, cocaine, methamphetamine and others.

Current pharmacological therapies for the treatment of the adverse health effects of stimulants such as METH relieve some organ-based symptoms caused by these harmful drugs. The abuse of methamphetamine (METH) is a significant societal problem in the United States and worldwide. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.Ĭompeting interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.įunding: This work was supported in part by grants National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute HL55375 (KIV), and NIH/National Institute on Drug Abuse DA018039 (ECP), and a grant from the Arkansas Biosciences Institute (KIV). Received: AugAccepted: NovemPublished: December 5, 2013Ĭopyright: © 2013 Peterson et al. PLoS ONE 8(12):Įditor: Jie Zheng, University of Akron, United States of America

The structural information reported here elucidates key molecular interactions important in anti-methamphetamine abuse immunotherapy.Ĭitation: Peterson EC, Celikel R, Gokulan K, Varughese KI (2013) Structural Characterization of a Therapeutic Anti-Methamphetamine Antibody Fragment: Oligomerization and Binding of Active Metabolites. Upon ligand binding, the CDR loops adopt a closed formation, encasing the drug almost completely. In the apo state the CDR loops of scFv6H4 form an open conformation of the binding pocket. Two of the histidine residues of each C-terminal His-tag interact with Ni 2+ in an octahedral geometry. We were also able to structurally characterize the coordination of the His-tags with Ni 2+. The apo structure forms a trimer in the crystal lattice and it results in the formation of an intermolecular composite beta-sheet with a three-fold symmetry. Here we report the crystal structure of scFv6H4 in homo-trimeric unbound (apo) form (2.60Å), as well as monomeric forms in complex with two active metabolites (+)-amphetamine (AMP, 2.38Å) and (+)-4-hydroxy methamphetamine (p-OH-METH, 2.33Å). We previously determined crystal structures of a high affinity anti-METH therapeutic single chain antibody fragment (scFv6H4, K D = 10 nM) in complex with METH and the (+) stereoisomer of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, or “ecstasy”). A key aspect of these immunotherapy strategies is the understanding of the subtle molecular interactions important for generating antibodies with high affinity and specificity for METH.
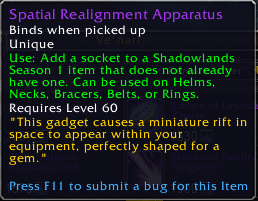
These immunotherapies work as pharmacokinetic antagonists, sequestering METH and its metabolites away from sites of action in the brain and reduce the rewarding and toxic effects of the drug.
UNBOUND REALITY FRAGMENT TRIAL
Vaccines and monoclonal antibodies (mAb) for treatment of (+)-methamphetamine (METH) abuse are in late stage preclinical and early clinical trial phases, respectively.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
